Selenium Cheat sheet
Author @rihemebh
Selenium
Selenium is an open source automated testing suite for web applications across different browsers and platforms. => It focuses on automation.
Selenium is not just a single tool but a suite of software's, each catering to different testing needs of an organization. It has 4 components:
- Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
- Selenium Remote Control (RC)
- WebDriver
- Selenium Grid
1. Selenium IDE
Selenium Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is the simplest framework in the Selenium suite and is the easiest one to learn. (record)
2. Selenium RC
3. Webdriver
WebDriver is a web automation framework that allows you to execute your tests against different browsers, WebDriver also enables you to use a programming language in creating your test scripts (not possible in Selenium IDE). It controls the browser from the OS level
WebDriver directly talks to the browser while Selenium RC needs the help of the RC Server in order to do so.
- Open Web Page
driver.get("https://google.com");
driver.navigate().to("http://www.insat.rnu.tn");
- Get URL
driver .getCurrentUrl();
- Get title
driver.getTitle();
- Forward , back , refrech the page
driver.navigate().back();
driver.navigate().forward();
driver.navigate().refresh();
- Switch
driver.switchTo().newWindow(WindowType.WINDOW);
driver.switchTo().newWindow(WindowType.TAB);
- Close
driver.close(); driver.quit();
- Windows management
// Size
driver.manage().getSize().getHeight();
driver.manage().getSize().getWidth();
//Position
driver.manage().setPosition(new Point(0,0));
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().window().minimize();
driver.manage().window().fullscreen();
//Screenshots
File screeenshotFile =((TakesScreenshot)driver).getScreenshotAs(OutputType.FILE);
4. Selenium Grid
Selenium grid is a tool used together with Selenium RC to run parallel tests across different machines and different browsers all at the same time. Parallele execution means running multiple test at one
JUnit
JUnit is an open source framework for the development and execution of automatable unit tests. The main interest is to ensure that the code still meets the needs even after possible modifications. More generally, this type of tests is called unit non-regression tests.
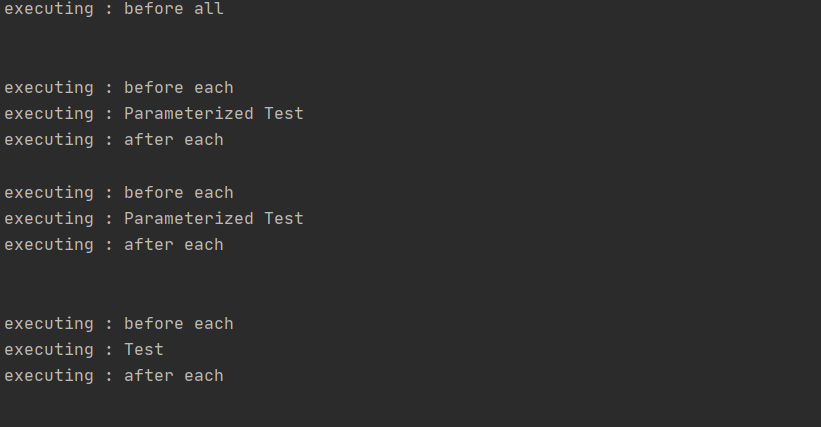
Annotations
| Annotation | Meaning | Usecase |
|---|---|---|
@BeforeClass | Run only once and specifically before anything else is run in the test class | initializes Selenium Webdriver and opens a browser |
@AfterClass | It is the annotation used to execute tasks after all the tests have been completed | close the browser and free that resource once all tests within the JUnit Selenium test class have been executed |
@BeforeEach | run code before each test | When writing a Selenium test class, there might be a mandatory step that starts the test from a specific web page. In that case, one can use the @Before annotation so that the required webpage is opened and ready before any test is run. |
@AfterEach | is used to run tasks after the execution of each test. After every test, the test results might have to be sent to a logging service or a monitoring service. | |
@Test | identify the actual test case | |
@RepeatedTest | run a given test any number of times | A web application is built to ensure caching does not occur due to highly dynamic data. So, each time the webpage is loaded, the cache must be empty. To automate the testing of this scenario, one has to run the same sequence multiple times. |
@ParameterizedTest | Parameterized test is to execute the same test over and over again using different values. |
Example :
// tells Selenium to set the timeout to 5 seconds
@Test(timeout=5000)
//@RepeatedTest takes in an integer which tells JUnit to run the test called “test” 6 times.
@RepeatedTest(6)
public void test()
{
// selenium test
}
Order of execution