Kerberos
Author @rihemebh
What is Kerberos
Kerberos is a computer-network authentication protocol that works on the basis of tickets to allow nodes communicating over a non-secure network to prove their identity to one another in a secure manner. Its designers aimed it primarily at a client–server model, and it provides mutual authentication—both the user and the server verify each other's identity. Kerberos protocol messages are protected against eavesdropping and replay attacks.
-- Wikipedia
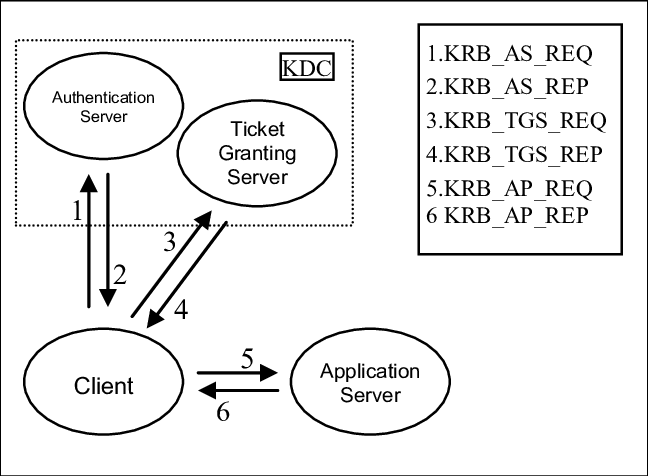
Architecture
What we will do ?
You will find in this repo a flask endpoint that needs kerberos authentication.
In order to test it you need to configure 3 machines : KDC, Client and Server then generate a token from the ticket produced by the KDC and everything will work properly
--Note: in the rest of this document I will only use 2 machines one for the KDC and the other will work as server and client
Prerequisite
- Docker
- Ubuntu image
- Python3
- Flask and Flask-Kerberos
How it works?
- Pull docker image :
docker pull ubuntu - Create network bridge to create a private netwok between containers so they can communicate with each others :
docker network create --driver=bridge <network name> - Create 2 containers from that image
Since the image doesn’t have any pre-installed dependencies you should first run :
apt update && apt upgrade
then install whatever you need (in our case we'll need: nano, host, ntp, ntpdate, python3, python3-pip )
Machines' Setup
We will use insat.tn as domain name.
In each machine match different ips to their sub domain name in
/etc/hosts172.21.0.2 kdc.insat.tn kdc
172.21.0.3 server.insat.tn serverTo test if everything is working properly try this command on each sub-domain:
host kdc.insat.tnSynchronize date between machines with ntp and ntpdate :
Why ?
- Kerberos is time sensitive. It uses timestamps mechanism to check the validity of a ticket.Thus, we will create our own time server and synchronize all the machines.
On the Kdc machine edit the
/etc/ntp.confand add the lines below:
restrict 127.0.0.1
restrict ::1
restrict 192.168.56.110 mask 255.255.255.0
nomodify notrap
server 127.127.1.0 stratum 10
listen on *- On the server install ntp and ntpdate:
apt install ntp
apt install ntpdate- then edit the
/etc/ntp.confand add the lines below:
pool ntp.ubuntu.com
server 192.168.56.110
server obelix- Synchronize time by running the below command on the server machine:
ntpdate -dv 192.168.56.110Configure KDC
apt install krb5-kdc krb5-admin-server krb5-config
When it's prompted : -> realm : INSAT.TN -> kerberos server : kdc.insat.tn -> Administrative Service: kdc.insat.tn
- Create the realm: A Kerberos realm is the domain over which a Kerberos authentication server has the authority to authenticate a user, host or service.
krb5_newrealm
- Create principals and generate keytab:
- A Kerberos Principal represents a unique identity in a Kerberos system to which Kerberos can assign tickets to access Kerberos-aware services.
- The Kerberos Keytab file contains mappings between Kerberos Principal names and DES-encrypted keys that are derived from the password used to log into the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC).
kadmin.local
addprinc root/admin
addprinc -randkey host/kdc.example.tn
ktadd host/kdc.example.tn
4. Configure Server
apt install krb5-user libpam-krb5 libpam-ccreds
Then do the same thing for realm, kerberos service, administrative service
- Add host :
kadmin
addprinc -randkey host/server.insat.tn
ktadd host/server.insat.tn
- Install Flask and Flask-Kerberos with pip
pip install flask
If you are using a docker image you should run those commands before installing flask kerberos:
apt-get install libkrb5-dev
apt-get install krb5-config
apt-get install libkrb5-dev
apt-get install libsasl2-dev
apt-get install libsasl2-modules-gssapi-mit
pip install requests_kerberos
pip install flask_kerberos
=> Now your machines are ready to use the flask service
Integrating Kerberos to a Flask Endpoint
Since Kerberos is based on ticket granting and not passwords so we need first to grant a ticket for the user to access the service
Tickets
We have 2 types of tickets
- TGT (ticket granting ticket) : the ticket that will allow you to get tickets for services
- TGS (ticket granting service) allow you to access a service secured by kerberos
Steps
In order to test the endpoint you need to follow these steps:
- Generate a ticket :
kinit. - Get the List of tickets with some details about them like expiration date :
klist. - Change the diffrent domain names in files "requestHandler" and "index" with your ones.
- Run the server
./index.py - Execute the requestHandler.py file : its role is to generate a negotiate token and add the header to the url.