ADO.NET
Author @rihemebh
ADO Stands for : ActiveX Data Object
It is a module of .Net Framework which is used to establish connection between application and data sources.
ADO.NET has two main components that are used for accessing and manipulating data are:
| Data provider | DataSet |
|---|---|
| It is used to connect to the database, execute commands and retrieve the record. | It is a collection of data tables that contain the data. It is used to fetch data without interacting with a Data Source that's why, it also known as disconnected data access method. |
Connected Mode
SqlConnection : It is used to establish a connection to a specific data source
SqlCommand : It is used to execute queries to perform database operations
SqlDataReader: It is used to read data from data source
SqlDataAdapter: It works as a bridge between a DataSet and a data source to retrieve data.It can be used to fill the DataSet and update the data source |
|---|
Disconnected Mode
DataSet: It is used to initialize a new instance of the DataSet class
Stored Procedures
After adding stored procedure in the sql server our SqlCommand becomes:
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand()
{
CommandText = "<stored procedure namme>",
Connection = connection_var,
CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure
};
//with parameters :
SqlParameter param = new SqlParameter
{
ParameterName = "@paramname",
SqlDbType = SqlDbType.<type>,
Value = "<VALUE>",
Direction = ParameterDirection.Input (or output)
};
cmd.Parameters.Add(param);
Entity Framework
Entity Framework (EF) is an open source object-relational mapping (ORM) framework for Ado.NET
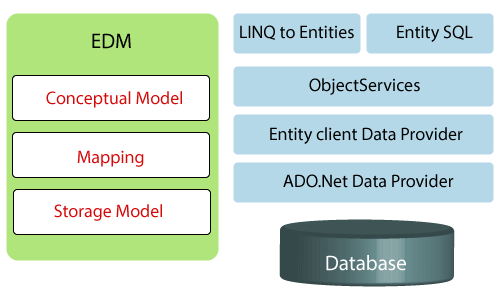 |EDM (Entity Data Model): It is a set of concepts that describe the structure of data Conceptual model
|EDM (Entity Data Model): It is a set of concepts that describe the structure of data Conceptual model
Mapping
Storage model.
LINQ to Entities: is a query language used to write queries against the object model. It returns entities, which are defined in the conceptual model.
| Entity SQL: is another query language just like LINQ to Entities. |
|---|
Workflow
| ModelFirst | DatabaseFirst | CodeFirst |
|---|---|---|
| Working on a visual diagram using the EF Designer and letting the Entity Framework create/update the rest accordingly | building the Database and letting Entity Framework create/update the rest accordingly | writing the Data Model entity classes and let Entity Framework generate the Database accordingly |
Code First
1- Create Models
- DataAnnotions : [annotions details]
| Key | Column("Name", TypeName="ntext") | ForignKey("fkname") | NotMapped |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specifies the primary key of the table | Specifies the column name and type | Foreign kety name | will not be mapped in the db |
- Relations :
1. One To One
class c1 {
public int id {get; set;}
public virtual c2 c {get; set;}
}
class c2 {
[Key, ForeignKey("c1")]
public int id {get; set;}
public virtual c1 c {get; set;}
}
2. One To Many
class c1 {
public int id {get; set;}
public virtual ICollection<c2> cs {get; set;}
}
class c2 {
public int id {get; set;}
public virtual c1 c {get; set;}
}
3. Many To Many
class c1 {
public int id {get; set;}
public virtual ICollection<c2> cs {get; set;}
}
class c2 {
public int id {get; set;}
public virtual ICollection<c1> c {get; set;}
}
2. Create a DBcontext for your database
you should first create a database in the sql server than add the connectionString to your dbcontext class
dbcontext calss
It is the primary class that is responsible for interacting with data as object. It often referred to as context. It is a wrapper around ObjectContext which is useful in all the development models: Code First, Model First and Database First.
- Role:
- Querying : converts database values into entity objects and vice versa.
- Change Tracking : It keeps track of changes occurred in the entities after it has been querying from the database.
- Persisting Data : It also performs the Insert, update and delete operations to the database, based on the entity states.
####### Example
public class ForumContext : DbContext
{ public DbSet<Category> Categories { get; set; }
public DbSet<Post> Posts { get; set; }
public DbSet<PostAnswer> PostAnswer { get; set; }
public DbSet<Tag> Tags { get; set; }
}
####### Methods Of DBContext
| Entry | Entry\<TEntity> | Set(Type) | Set\<TEntity>() | SaveChanges() |
|---|
####### Methods Of DBSet
| Add | Attach(Entity) | Create | Find(int) | Include | Remove | SqlQuery |
|---|
3- Migrations
Database Initilisations
Entity framework Code First had different database initialization strategies prior to EF 4.3 like:
CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsDropCreateDatabaseIfModelChangesDropCreateDatabaseAlways
Automated Migrations
In your package manager tap those cmd:
- enable-migrations
- add-migration "migration_name" : this will create a migration for you that has 2 methods
- up() contains all the sql queries of the changes that you made
- down() : contains the opposite of the up() method
- update-database :This helps you add all the updates to your server
EDM
- EDM Structure :
- EntityContainer : EntityContainer EntityContainer is a wrapper for EntitySets and AssociationSets . It is an entry point for querying the model.
- EntitySet : Container for EntityType (like the db table)
- EntityType : datatype in the model
- AssociationSet : Defines the relation between each entityset
Quering with EDM
LinQ to Entity
- LinQ Method
//Student is a model
using( var context = new SchoolDBStudents() ) {
var query = context.Students.Where(s=>s.StudentName == "Bill").FirstOrDefault<Student>();
}
- LinQ Query
```csharp
using( var context = new SchoolDBStudents() ) {
var query = from st in context.Students
where st.StudentName = "Bill"
select st;
var student = query.FirstOrDefault<Student>();
}
-Projection
| First/FirstOrDefault | Single/SingleOrDefault | ToList | GroupBy | OrderBy |
|---|
|Returns the first row from the query result
The difference = First() will throw an exception and FirstOrDefault () returns default value (null) if there is no result data|when we are sure that the result would contain only one element
Single or SingleOrDefault will throw anexception, if the result contains more than one element.|Converts the result to a list|Groups the result by a creteria|Sort the result by a criteria|
- Entity SQL : It returns ObjectQuery instead of Iqueryable
//You need ObjectContext to create a query using Entity SQL.
string command = " select VALUE st from SchoolDBEntities.Students " +
"AS st WHERE st.StudentName == 'Bill'";
var obj = (ctx as IObjectContextAdapter).ObjectContext;
ObjectQuery<Student> student = obj.CreateQuery<Student>(command);
}
- Native SQL
using( var ctx = new SchoolDBEntities() ) {
var student = ctx.Students.SqlQuery("Select * from Students where StudentId=@id", new SqlParameter('@id',1)).FirstOrDefault();
}
Operations
Using DBContext
1. Insert
// create new Standard entity object
var newStandard = new Standard();
// Assign standard name
newStandard.StandardName = "Standard1 ";
//create DBContext object
using (var dbCtx = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
//Add standard object into Standard DBset
dbCtx.Standards.Add(newStandard);
// call SaveChanges method to save standard into database
dbCtx.SaveChanges();
}
2. Update
Student stud ;
// Get student from DB
using (var ctx = new SchoolDBEntities())
{ stud = ctx.Students.Where(s => s.StudentName == "New
Student1").FirstOrDefault<Student>();
}
// change student name in disconnected mode (out of DBContext scope)
if (stud != null) { stud.StudentName = "Updated Student1"; }
//save modified entity using new DBContext
using (var dbCtx = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
//Mark entity as modified
dbCtx.Entry(stud).State = System.Data.EntityState.Modified;
dbCtx.SaveChanges();
}
3. Delete
using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities())
{
context.Entry(disconnectedTeacher).State =
System.Data.EntityState.Deleted;
context.SaveChanges();
}